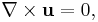Velocity potential
A velocity potential is used in fluid dynamics, when a fluid occupies a simply-connected region and is irrotational. In such a case,
where 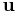 denotes the flow velocity of the fluid. As a result,
denotes the flow velocity of the fluid. As a result, 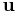 can be represented as the gradient of a scalar function
can be represented as the gradient of a scalar function  :
:
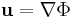 ,
,
 is known as a velocity potential for
is known as a velocity potential for 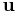 .
.
A velocity potential is not unique. If 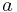 is a constant then
is a constant then 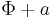 is also a velocity potential for
is also a velocity potential for 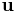 . Conversely, if
. Conversely, if 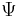 is a velocity potential for
is a velocity potential for 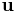 then
then  for some constant
for some constant 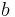 . In other words, velocity potentials are unique up to a constant.If value of Φ satisfies Laplace equation,it indicates case of fluid flow.
. In other words, velocity potentials are unique up to a constant.If value of Φ satisfies Laplace equation,it indicates case of fluid flow.
Unlike a stream function, a velocity potential can exist in three-dimensional flow.